前言 一般的文档编辑器都会提供一个主菜单(Menu),主菜单中包含一些菜单项(MenuItem),每个菜单项包含很多的命令操作,包括打开命令,创建命令,编辑命令等等,要设计这样的文档编辑系统,可以考虑使用命令模式。
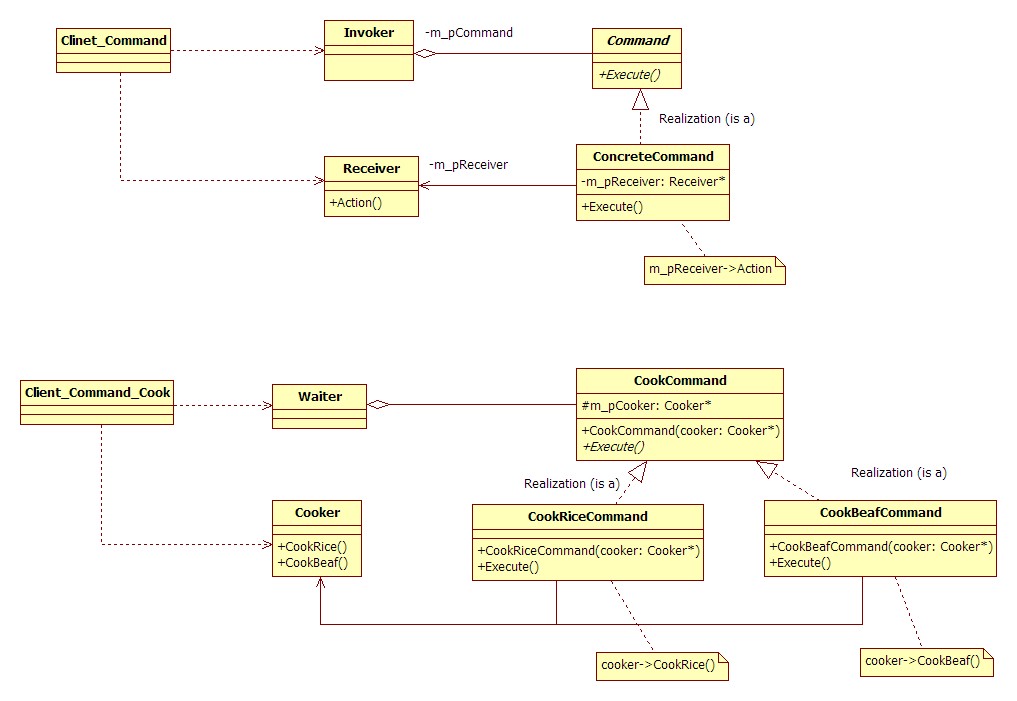
命令模式 意图 将一个请求封装为一个对象,从而使你可用不同的请求对客户进行参数化;对请求排队或记录请求日志,以及支持可撤销的操作,别名为动作(Action)模式或事务(Transaction)模式
命令模式可以将请求发送者和接收者完全解耦,发送者与接收者之间没有直接引用关系,发送请求的对象只需要知道如何发送请求,而不必知道如何完成请求
参与者
Command
ConcreteCommand
Invoker
Receiver
Client
模式结构
代码实现 1.首先定义接收者Receiver,并提供Action()接口:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Receiver { public : void Action () { cout << "Receiver: Action!" << endl; } };
2.再定义抽象命令类Command,并提供公共接口Execute():
1 2 3 4 5 6 class Command { public : virtual void Execute ()0 ; };
3.再定义Command类的一个具体命令子类,并实现其中的Execute()接口,持有命令接收者的对象,该接口主要作用是调用不同接收者Receiver的Action()方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class ConcreteCommand : public Command { private : Receiver *m_pReceiver; public : ConcreteCommand(Receiver *prec) : m_pReceiver(prec) {}; public : void Execute() { m_pReceiver->Action(); } };
4.定义一个命令调用者,持有抽象命令对象,并提供一个Invoke()接口,供客户端调用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Invoker{ private : Command *m_pCommand; public: Invoker(Command * pcmd ) : m_pCommand(pcmd ) {}; public: void Invoke() { m_pCommand->Execute() ; } };
5.测试命令模式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 void CommandTest_General() { Receiver *pR = new Receiver() ; Command *pC = new ConcreteCommand(pR ) ; Invoker *pI = new Invoker(pC ) ; pI->Invoke() ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(pR ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(pC ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(pI ) ; }
4.运行结果:
Receiver: Action!
命令模式的分类 命令模式根据应用的使用场景,可以分为以下几类:
一般场景命令模式 即一般场景下的请求发送者和请求接收处理者解耦,一般一个请求对应于一个请求处理
命令队列 将多个请求排队,当一个请求发送者发送一个请求时,将不止一个请求接收者产生响应,这些请求接收者将逐个执行业务方法,完成对请求的处理CommandQueue类,由该类来负责存储多个命令对象,而不同的命令对象可以对应不同的请求接收者,代码实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class CommandQueue{ private : list <Command*> _listCommand; public: void addCommand(Command &cmd ) { _listCommand ._back(&cmd ) ; } void removeCommand(Command &cmd ) { _listCommand . } void Execute() { for (list <Command*>::iterator it = _listCommand .begin () ; it!= _listCommand .end () ; ++it) { (*it)->Execute() ; } } }; class CommandQueueInvoker{ private : CommandQueue *_commandQueue; public: CommandQueueInvoker(CommandQueue &cmdQueue ) :_commandQueue(&cmdQueue ) {}; void setCommandQueue(CommandQueue &cmdQueue ) { _commandQueue = &cmdQueue; } void Invoke() { _commandQueue->Execute() ; } };
命令队列与“批处理”有点类似。批处理—可以对一组对象(命令)进行批量处理,当一个发送者发送请求后,将有一系列接收者对请求作出响应
带有撤销操作的命令模式 在命令模式中,我们可以通过调用一个命令对象的execute()方法来实现对请求的处理,如果需要撤销(Undo)请求,可通过在命令类中增加一个逆向操作来实现,
实现计算机加减乘除操作,并带有撤销操作
1.首先定义命令接受者,即各种操作业务的具体实现者:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Adder { public : float add(float leftOperand, float rightoperand) { cout << leftOperand << " add " << rightoperand << endl; return (leftOperand + rightoperand); } }; class Minuser { public : float minus(float leftOperand, float rightoperand) { cout << leftOperand << " minus " << rightoperand << endl; return (leftOperand - rightoperand); } }; class Multiplater { public : float multiplate(float leftOperand, float rightoperand) { cout << leftOperand << " multiplate " << rightoperand << endl; return (leftOperand * rightoperand); } }; class Diviser { public : float dive(float leftOperand, float rightoperand) { assert(0 != rightoperand); cout << leftOperand << " dive " << rightoperand << endl; return (leftOperand / rightoperand); } };
2.定义抽象命令对象,和具体的命令对象,分别提供和实现compute()和unCompute()两种方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 class ComputerCommand { public : virtual float compute(float leftOperand, float rightOperand) = 0 ; virtual float unCompute(float leftOperand, float rightOperand) = 0 ; }; class AddCommand : public ComputerCommand { private : Adder *_adder; float _result; public : AddCommand(Adder *adder) : _adder(adder), _result(0 ) {}; public : virtual float compute(float leftOperand, float rightOperand) { _result = _adder->add(leftOperand, rightOperand); return _result; } virtual float unCompute(float leftOperand, float rightOperand) { _result = _adder->add(leftOperand, -rightOperand); return _result; } }; class MinusCommand : public ComputerCommand { private : Minuser *_minuser; float _result; public : MinusCommand(Minuser *minuser) : _minuser(minuser), _result(0 ) {}; public : virtual float compute(float leftOperand, float rightOperand) { _result = _minuser->minus(leftOperand, rightOperand); return _result; } virtual float unCompute(float leftOperand, float rightOperand) { _result = _minuser->minus(leftOperand, -rightOperand); return _result; } }; class MultiplateCommand : public ComputerCommand { private : Multiplater *_multiplater; float _result; public : MultiplateCommand(Multiplater *multiplater) : _multiplater(multiplater) , _result(0 ) {}; public : virtual float compute(float leftOperand, float rightOperand) { _result = _multiplater->multiplate(leftOperand, rightOperand); return _result; } virtual float unCompute(float leftOperand, float rightOperand) { _result = _multiplater->multiplate(leftOperand, 1 /rightOperand); return _result; } }; class DiveCommand : public ComputerCommand { private : Diviser *_diviser; float _result; public : DiveCommand(Diviser *diviser) : _diviser(diviser), _result(0 ) {}; public : virtual float compute(float leftOperand, float rightOperand) { _result = _diviser->dive(leftOperand, rightOperand); return _result; } virtual float unCompute(float leftOperand, float rightOperand) { _result = _diviser->dive(leftOperand, 1 /rightOperand); return _result; } };
3.命令的调用者,持有两个stack,分别为撤销操作命令和恢复撤销操作命令:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 class ComputerInvoker { private : ComputerCommand *_currentComputerCommand ; stack<ComputerCommand*> _stackUndoCommand ; stack<ComputerCommand*> _stackRedoCommand ; float _computeResult ; public: ComputerInvoker(ComputerCommand *cmd) : _currentComputerCommand (cmd), _computeResult (0 ) {}; public: void setComputerCommand(ComputerCommand *cmd) { _currentComputerCommand = cmd; } void invokeCompute(float operand) { _computeResult = _currentComputerCommand ->compute(_computeResult , operand); _stackUndoCommand .push(_currentComputerCommand ); cout << "normal compute: result is : " << _computeResult << endl ; } void invokeUncompute(float operand) { if (_stackUndoCommand .empty()) { cout << "undo command stack is empty!" << endl ; return; } _currentComputerCommand = _stackUndoCommand .top(); _stackUndoCommand .pop(); _computeResult = _currentComputerCommand ->unCompute(_computeResult , operand); _stackRedoCommand .push(_currentComputerCommand ); cout << "undo compute: result is : " << _computeResult << endl ; } void invokeRecompute(float operand) { if (_stackRedoCommand .empty()) { cout << "resume do command stack is empty!" << endl ; return; } _currentComputerCommand = _stackRedoCommand .top(); _stackRedoCommand .pop(); _computeResult = _currentComputerCommand ->compute(_computeResult , operand); _stackUndoCommand .push(_currentComputerCommand ); cout << "redo compute: result is : " << _computeResult << endl ; } float getComputeResult() { return _computeResult ; } };
4.测试带有撤销操作的命令模式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 void CommandTest_Compute() { Adder *adder = new Adder() ; ComputerCommand *addCmd = new AddCommand(adder ) ; Minuser *minuser = new Minuser() ; ComputerCommand *minusCmd = new MinusCommand(minuser ) ; Multiplater *multiplater = new Multiplater() ; ComputerCommand *multiplateCmd = new MultiplateCommand(multiplater ) ; Diviser *diviser = new Diviser() ; ComputerCommand *diveCmd = new DiveCommand(diviser ) ; ComputerInvoker *computeInvoke = new ComputerInvoker(addCmd ) ; computeInvoke->invokeCompute(50) ; computeInvoke->setComputerCommand(minusCmd ) ; computeInvoke->invokeCompute(20) ; computeInvoke->setComputerCommand(multiplateCmd ) ; computeInvoke->invokeCompute(3) ; computeInvoke->setComputerCommand(diveCmd ) ; computeInvoke->invokeCompute(9) ; computeInvoke->setComputerCommand(addCmd ) ; computeInvoke->invokeCompute(10) ; cout << "*** last normal compute result is : " << computeInvoke->getComputeResult() << " ***" << endl; computeInvoke->invokeUncompute(10) ; computeInvoke->invokeUncompute(9) ; computeInvoke->invokeUncompute(3) ; computeInvoke->invokeUncompute(20) ; computeInvoke->invokeUncompute(50) ; cout << "*** last undo compute result is : " << computeInvoke->getComputeResult() << " ***" << endl; computeInvoke->invokeRecompute(50) ; computeInvoke->invokeRecompute(20) ; computeInvoke->invokeRecompute(3) ; computeInvoke->invokeRecompute(9) ; computeInvoke->invokeRecompute(10) ; cout << "*** last redo compute result is : " << computeInvoke->getComputeResult() << " ***" << endl; float finalResult = computeInvoke->getComputeResult() ; cout << "*** final compute result is " << finalResult << " ***" << endl; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(adder ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(minuser ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(multiplater ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(diviser ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(addCmd ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(minusCmd ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(multiplateCmd ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(diveCmd ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(computeInvoke ) ; }
5.运行结果:
0 add 50
normal compute: result is : 50
50 minus 20
normal compute: result is : 30
30 multiplate 3
normal compute: result is : 90
90 dive 9
normal compute: result is : 10
10 add 10
normal compute: result is : 20
\*\*\* last normal compute result is : 20 \*\*\*
20 add -10
undo compute: result is : 10
10 dive 0.111111
undo compute: result is : 90
90 multiplate 0.333333
undo compute: result is : 30
30 minus -20
undo compute: result is : 50
50 add -50
undo compute: result is : 0
\*\*\* last undo compute result is : 0 \*\*\*
0 add 50
redo compute: result is : 50
50 minus 20
redo compute: result is : 30
30 multiplate 3
redo compute: result is : 90
90 dive 9
redo compute: result is : 10
10 add 10
redo compute: result is : 20
\*\*\* last redo compute result is : 20 \*\*\*
\*\*\* final compute result is 20 \*\*\*
请求日志的命令模式 请求日志就是将请求的历史记录保存下来,通常以日志文件(Log File)的形式永久存储在计算机中
1.可以为系统提供一种恢复机制,在请求日志文件中可以记录用户对系统的每一步操作,从而让系统能够顺利恢复到某一个特定的状态
在上面带恢复功能的简易计算器基础上增加请求日志功能
1.增加操作命令日志的list:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 typedef struct tag_computeLog { ComputerCommand* cmd; float leftOperand; float rightOperand; }computeLog; list<computeLog> _listComputeLogCommand;
2.修改调用执行计算的方法,在其中添加command到list:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 void invokeCompute(float operand) { computeLog log ; log .cmd = _currentComputerCommand ; log .leftOperand = _computeResult ; log .rightOperand = operand; _listComputeLogCommand .push_back(log ); _computeResult = _currentComputerCommand ->compute(_computeResult , operand); ... }
3.增加新的日志命令操作,循环调用操作command记录list中的命令:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 void invokeLogCommand(void ){ _computeResult = 0 ; for (list <computeLog>::iterator it = _listComputeLogCommand.begin(); it != _listComputeLogCommand.end(); ++it ) { _computeResult =((*it ).cmd->compute((*it ).leftOperand, (*it ).rightOperand)); } }
宏命令 宏命令(Macro Command)又称为组合命令,它是组合模式和命令模式联用的产物。宏命令是一个具体命令类,它拥有一个集合属性,在该集合中包含了对其他命令对象的引用。通常宏命令不直接与请求接收者交互,而是通过它的集合成员来调用接收者的方法
宏命令的execute()方法时,将递归调用它所包含的每个成员命令的execute()方法
在上面带恢复和日志功能的简易计算器基础上增加宏命令(批处理,依次调用各个命令)
1.修改抽象命令类ComputerCommand,增加增加和删除命令集合元素的操作:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class ComputerCommand { public : virtual float compute (float leftOperand, float rightOperand) 0 ; virtual float unCompute (float leftOperand, float rightOperand) 0 ; public : virtual void insertCommand (ComputerCommand *cmd) virtual void removeCommand (ComputerCommand *cmd) ComputerCommand* getCommand (int i) { return NULL ; } };
2.增加宏命令具体类MacroCommand,继承于抽象命令类ComputerCommand,并实现其各个方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 class MacroCommand : public ComputerCommand{ private : vector<ComputerCommand*> _vecCmd; public : MacroCommand () {}; public : void insertCommand (ComputerCommand *cmd) { _vecCmd.push_back (cmd); } void removeCommand (ComputerCommand *cmd) { for (vector<ComputerCommand*>::iterator it = _vecCmd.begin (); it != _vecCmd.end (); ++it) { if (*it == cmd) { _vecCmd.erase (it); } } } ComputerCommand* getCommand (int i) { assert (i < _vecCmd.size ()); return _vecCmd[i]; }; float compute (float leftOperand, float rightOperand) { float result = 0 ; for (vector<ComputerCommand*>::iterator it = _vecCmd.begin (); it != _vecCmd.end (); ++it) { result += (*it)->compute (leftOperand, rightOperand); } return result; } float unCompute (float leftOperand, float rightOperand) { float result = 0 ; for (vector<ComputerCommand*>::iterator it = _vecCmd.begin (); it != _vecCmd.end (); ++it) { result += (*it)->unCompute (leftOperand, rightOperand); } return result; } };
3.使用宏命令,与使用简单命令类似,只是使用前,先添加命令元素:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Adder *adder = new Adder() ; ComputerCommand *addCmd = new AddCommand(adder ) ; Minuser *minuser = new Minuser() ; ComputerCommand *minusCmd = new MinusCommand(minuser ) ; Multiplater *multiplater = new Multiplater() ; ComputerCommand *multiplateCmd = new MultiplateCommand(multiplater ) ; Diviser *diviser = new Diviser() ; ComputerCommand *diveCmd = new DiveCommand(diviser ) ; ComputerCommand *macroCmd = new MacroCommand() ; macroCmd->insertCommand(addCmd ) ; macroCmd->insertCommand(minusCmd ) ; macroCmd->insertCommand(multiplateCmd ) ; macroCmd->insertCommand(diveCmd ) ; computeInvoke->setComputerCommand(macroCmd ) ; computeInvoke->invokeCompute(2) ;
使用场景
系统需要将请求调用者和请求接收者解耦,使得调用者和接收者不直接交互。请求调用者无须知道接收者的存在,也无须知道接收者是谁,接收者也无须关心何时被调用
系统需要在不同的时间指定请求、将请求排队和执行请求。一个命令对象和请求的初始调用者可以有不同的生命期,换言之,最初的请求发出者可能已经不在了,而命令对象本身仍然是活动的,可以通过该命令对象去调用请求接收者,而无须关心请求调用者的存在性,可以通过请求日志文件等机制来具体实现
系统需要支持命令的撤销(Undo)操作和恢复(Redo)操作
系统需要将一组操作组合在一起形成宏命令
优缺点
优点
降低系统的耦合度。由于请求者与接收者之间不存在直接引用,因此请求者与接收者之间实现完全解耦
新的命令可以很容易地加入到系统中
缺点
命令模式具体实例 编辑器操作问题 使用命令模式简单实现前言所述的文档编辑器简单操作功能
代码实现 DocCommand:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class DocCommand { public : DocCommand () {}; virtual ~DocCommand () {}; public : virtual void execute (void ) 0 ; virtual void unexecute (void ) 0 ; virtual void addDocCommand (DocCommand* doc) virtual void removeDocCommand (DocCommand* doc) virtual Document* getCurrentOpenDoc (void ) return NULL ; } };
2.分别定义命令类DocCommand的子类OpenDocCommand和EditDocCommand和SaveDocCommand和CloseDocCommand及宏命令MacroDocCommand:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 class OpenDocCommand : public DocCommand { public : OpenDocCommand (Application *app) : _app (app), _currentOpenDoc (NULL ), _response ("" public : void execute (void { askUser (); if (!_response.empty ()) { _currentOpenDoc = _app->getDocByName (_response); if (NULL != _currentOpenDoc) { _currentOpenDoc->open (); } } } void unexecute (void { cout << "can not unexecute open operate!!!" << endl; } private : void askUser ( { char confirm; cout << "please input a name for the doc: " << endl; cin >> _response; cout << "you have enter a doc named: " << _response << endl; cout << "confirm? (Y/N)" << endl; cin >> confirm; switch (confirm) { case 'y' : case 'Y' : break ; case 'N' : case 'n' : default : _response = "" ; break ; } }; public : Document * getCurrentOpenDoc (void { return _currentOpenDoc; } private : Application *_app; Document *_currentOpenDoc; string _response; }; class EditDocCommand : public DocCommand { public : EditDocCommand (Document * doc) : _doc (doc ) {}; public : void execute (void { if (NULL != _doc) { _doc->edit (); } } void unexecute (void { if (NULL != _doc) { _doc->unedit (); } } Document * getCurrentOpenDoc (void { return _doc; } private : Document *_doc; }; class SaveDocCommand : public DocCommand { public : SaveDocCommand (Document * doc) : _doc (doc ) {}; public : void execute (void { if (NULL != _doc) { _doc->save (); } } void unexecute (void { if (NULL != _doc) { _doc->unsave (); } } Document * getCurrentOpenDoc (void { return _doc; } private : Document *_doc; }; class CloseDocCommand : public DocCommand { public : CloseDocCommand (Document * doc) : _doc (doc ) {}; public : void execute (void { if (NULL != _doc) { _doc->close (); } } void unexecute (void { cout << "can not unexecute close operate!!!" << endl; } Document * getCurrentOpenDoc (void { return _doc; } private : Document *_doc; }; class MacroDocCommand : public DocCommand { public : MacroDocCommand () {}; public : void execute (void { for (list<DocCommand *>::iterator it = _listDoc.begin (); it != _listDoc.end (); ++it) { (*it)->execute (); } } void unexecute (void { for (list<DocCommand *>::iterator it = _listDoc.begin (); it != _listDoc.end (); ++it) { (*it)->unexecute (); } } public : void addDocCommand (DocCommand* doc ) { _listDoc.push_back (doc); } void removeDocCommand (DocCommand* doc ) { _listDoc.remove (doc); } private : list<DocCommand *> _listDoc; };
3.定义命令的接收者即,实际业务的实现者Document和Application:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 class Document{ private : string _name; public: Document(string name ) :_name(name ) {}; public: void open (void) { cout << "open document " << _name << endl; } void edit(void) { cout << "edit document " << _name << endl; } void save(void) { cout << "save document " << _name << endl; } void close(void) { cout << "close document " << _name << endl; } void unedit(void) { cout << "unedit document " << _name << endl; } void unsave(void) { cout << "unsave document " << _name << endl; } string getName(void ) { return _name; } }; class Application{ private : list <Document*> _listDoc; string _appName; public: Application(string name ) : _appName(name ) {}; virtual ~Application() { for (list <Document*>::iterator it = _listDoc .begin () ; it != _listDoc .end () ; ++it) { delete *it; *it = NULL; } } public: bool isExitDocByName(string name ) { for (list <Document*>::iterator it = _listDoc .begin () ; it != _listDoc .end () ; ++it) { if (0 == ((*it)->getName() .compare(name))) { return true ; } } return false ; } Document* getDocByName(string name ) { for (list <Document*>::iterator it = _listDoc .begin () ; it != _listDoc .end () ; ++it) { if (0 == ((*it)->getName() .compare(name))) { return *it; } } Document *doc = new Document(name ) ; addDoc(doc ) ; return doc; } string getName(void ) { return _appName; } private : void addDoc(Document* doc ) { _listDoc ._back(doc ) ; } };
4.最后定义命令请求的调用者Writer:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 class Writer{ public: Writer(string name ) : _name(name ) {}; virtual ~Writer() { for (list <DocCommandLog*>::iterator it = _listHistoryCmdLog .begin () ; it != _listHistoryCmdLog .end () ; ++it) { delete *it; *it = NULL; } } public: class DocCommandLog { public: DocCommand *docCmd; bool isexecute; }; void setDocCommand(DocCommand * cmd ) { _currentCmd = cmd; } void do Work(void ) { _currentCmd->execute() ; DocCommandLog *cmdLog = new DocCommandLog() ; cmdLog->docCmd = _currentCmd; cmdLog->isexecute = true ; _listHistoryCmdLog ._back(cmdLog ) ; } void undoWork(void ) { _currentCmd->unexecute() ; DocCommandLog *cmdLog = new DocCommandLog() ; cmdLog->docCmd = _currentCmd; cmdLog->isexecute = false ; _listHistoryCmdLog ._back(cmdLog ) ; } void batWorkByHistoryCmdLog(void ) { for (list <DocCommandLog*>::iterator it = _listHistoryCmdLog .begin () ; it != _listHistoryCmdLog .end () ; ++it) { if ((*it)->isexecute) { (*it)->docCmd->execute() ; } else { (*it)->docCmd->unexecute() ; } } } public: string getName(void ) { return _name; } private : string _name; DocCommand *_currentCmd; list <DocCommandLog*> _listHistoryCmdLog; };
5.测试命令模式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 void CommandTest_Doc() { Application *app = new Application("VS 2015" ) ; cout << "app name is : " << app->getName() << endl; Writer *writer = new Writer("tly" ) ; cout << "writer name is: " << writer->getName() << endl; DocCommand *openCmd = new OpenDocCommand(app ) ; writer->setDocCommand(openCmd ) ; writer->do Work() ; Document *currentOpenDoc = openCmd->getCurrentOpenDoc() ; if (NULL == currentOpenDoc) { cout << "not open any doc !!!" << endl; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(openCmd ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(writer ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(app ) ; return; } DocCommand *editCmd = new EditDocCommand(currentOpenDoc ) ; writer->setDocCommand(editCmd ) ; writer->do Work() ; writer->undoWork() ; DocCommand *macroCmd = new MacroDocCommand() ; DocCommand *saveCmd = new SaveDocCommand(currentOpenDoc ) ; macroCmd->addDocCommand(saveCmd ) ; DocCommand *closeCmd = new CloseDocCommand(currentOpenDoc ) ; macroCmd->addDocCommand(closeCmd ) ; writer->setDocCommand(macroCmd ) ; writer->do Work() ; cout << "bat history log: " << endl; writer->batWorkByHistoryCmdLog() ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(openCmd ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(editCmd ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(saveCmd ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(closeCmd ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(macroCmd ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(writer ) ; SAFE_RELASE_POINTER(app ) ; }
6.运行结果:
app name is : VS 2015
writer name is: tly
please input a name for the doc:
design_pattern
you have enter a doc named: design_pattern
confirm? (Y/N)
y
open document design_pattern
edit document design_pattern
unedit document design_pattern
save document design_pattern
close document design_pattern
bat history log:
please input a name for the doc:
design_pattern
you have enter a doc named: design_pattern
confirm? (Y/N)
y
open document design_pattern
edit document design_pattern
unedit document design_pattern
save document design_pattern
close document design_pattern